Glaucoma Management: Protecting Your Vision
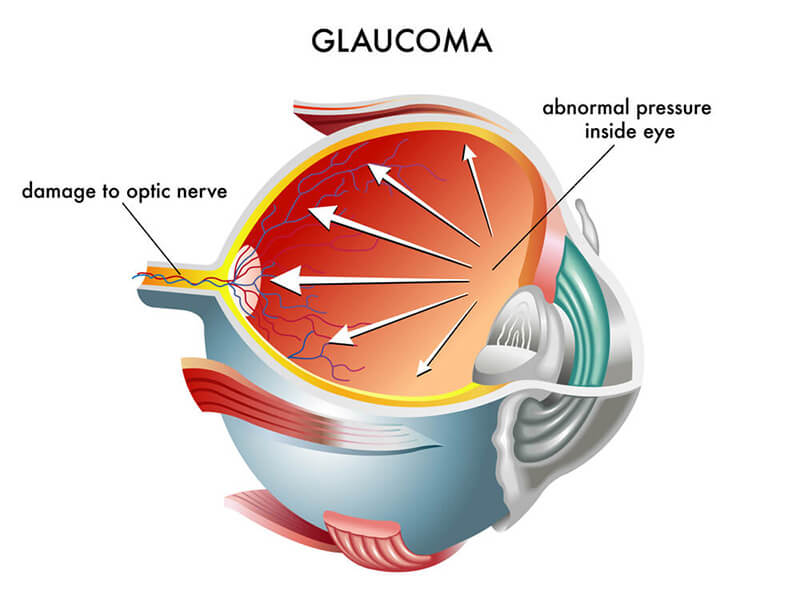
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased intraocular pressure (IOP), and can lead to irreversible vision loss if untreated. Early detection and effective management are crucial for preserving vision and preventing further damage.
👁️ Types of Glaucoma
1️⃣ Open-Angle Glaucoma – The most common type, where the eye's drainage canals become clogged over time, gradually increasing eye pressure.
2️⃣ Angle-Closure Glaucoma – Occurs when the drainage angle of the eye is blocked, causing a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure.
3️⃣ Normal-Tension Glaucoma – Optic nerve damage occurs despite normal eye pressure, likely due to poor blood flow to the optic nerve.
4️⃣ Congenital Glaucoma – Present at birth, caused by developmental abnormalities in the eye’s drainage system.
5️⃣ Secondary Glaucoma – Caused by another condition such as diabetes, eye injury, or the use of corticosteroids.
🔍 Diagnosis of Glaucoma
✔ Eye Pressure Test (Tonometry): Measures intraocular pressure to check for elevated levels.
✔ Optic Nerve Exam: A thorough eye exam to detect damage to the optic nerve.
✔ Visual Field Test: Assesses peripheral vision, which is often the first area affected by glaucoma.
✔ Gonioscopy: Examines the angle of the eye where the iris meets the cornea to assess drainage.
✔ Pachymetry: Measures corneal thickness, which can influence eye pressure readings.
💊 Treatment and Management Options
- Medications
✔ Eye Drops: The first line of treatment, aimed at reducing eye pressure. There are various types, such as:
- Prostaglandin analogs (e.g., latanoprost) – Increase fluid drainage from the eye.
- Beta-blockers (e.g., timolol) – Decrease the production of fluid.
- Alpha agonists (e.g., brimonidine) – Reduce fluid production and increase drainage.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., dorzolamide) – Lower fluid production.
- Rho kinase inhibitors (e.g., netarsudil) – Improve fluid outflow.
✔ Oral Medications: For cases where eye drops are insufficient or in addition to topical treatments.

- Surgical Treatment
✔ Trabeculectomy: A surgical procedure where part of the trabecular meshwork is removed to allow fluid to drain and reduce IOP.
✔ Glaucoma Drainage Implants: Tiny tubes are implanted to help fluid drain from the eye and lower pressure.
✔ Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS): Newer, less invasive techniques designed to lower IOP with fewer risks and quicker recovery.⏳ Ongoing Management and Lifestyle
✔ Regular Eye Exams: Glaucoma is often asymptomatic until significant damage occurs, so regular eye exams are critical for early detection and monitoring.
✔ Adherence to Treatment: Consistent use of prescribed medications is essential for controlling eye pressure.
✔ Healthy Lifestyle:- Stay active and maintain a healthy weight.
- Eat a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Limit caffeine intake, which can increase eye pressure.
✔ Protect Your Eyes: Wear protective eyewear to prevent injury, which can worsen glaucoma.
🎯 The Goal of Glaucoma Management
✅ Lower and control eye pressure
✅ Prevent optic nerve damage
✅ Preserve vision and quality of lifeAlthough glaucoma cannot be cured, with proper treatment and monitoring, it can be managed effectively, allowing people to lead normal, healthy lives. If you have a family history of glaucoma or are at risk, regular eye exams and early intervention are essential to preserving your vision.